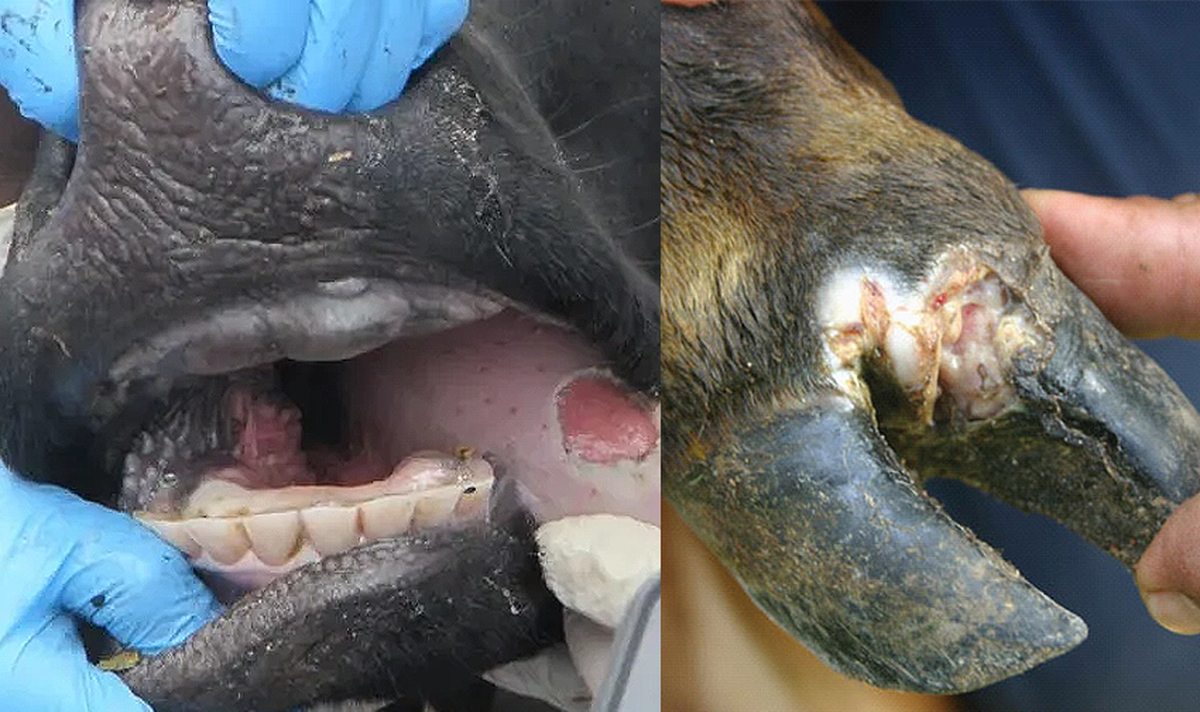
Foot and Mouth Disease (FMD) is a severe viral illness that primarily affects cattle, sheep, goats, and pigs. It is characterized by the sudden onset of fever, followed by the appearance of painful blisters or sores in the mouth, on the tongue, and around the hooves. These lesions cause lameness and difficulty eating, which can lead to reduced milk production and weight loss in affected animals.
The disease spreads rapidly through direct contact with infected animals, contaminated feed, water, and equipment. Airborne transmission is also possible under certain conditions, making FMD highly contagious and challenging to control.
Preventing FMD involves strict biosecurity measures such as isolating new or sick animals, disinfecting equipment, and controlling movement between farms. Vaccination programs play a crucial role in protecting livestock populations. Prompt diagnosis and veterinary intervention are essential to managing outbreaks effectively.
Farmers are advised to stay vigilant and immediately report any suspicious symptoms to local veterinary authorities to prevent widespread transmission. Awareness and education about FMD can significantly reduce economic losses and protect animal health.